The development of aerogel
In 1999, NASA developed silica aerogel with a density of 3 milligrams per cubic centimetre, making it the world's lightest solid material.
In 2011, American scientists collaborated to create an aerogel made of nickel, with a density of 0.9 milligrams per cubic centimetre, making it the lightest solid material at the time.
Aerogels made of nickel are placed on dandelion flowers, and the soft nap barely deforms
In July 2012, scientists from the university of Kiel in the United Kingdom and the university of science and technology in Hamburg, Germany, developed "flying graphite", the world's lightest material at the time, with a density of only 0.2mg/cm3. It looks like a black opaque sponge. "Flying graphite" is a network of porous carbon tubes interwoven in three dimensions at the nanometer and micron scales. Although it is light in weight, it is very elastic and has a strong compression resistance and tension load. It can be compressed by 95% and then restored to its original size. It also absorbs almost all light.
In 2013, the density of "all-carbon aerogel" developed by zhejiang university was 0.16 milligrams per cubic centimetre, setting a new record.
Academician of jian-yun yu 2015, donghua university, professor Ding Bin nanofibers with research team using ordinary fiber membrane materials developed a lightweight, super elastic fiber aerogel, authenticated by the Chinese measurement results show that the fiber of the aerogel solid material density is only 0.12 mg per cubic centimeter, a volume of 20 cubic centimeter of aerogel "fiber" can easily "on" a few root hairs on down.
In 2016, the team led by yu jianyong, academician of donghua university, and professor ding bin made a breakthrough in the research of carbon based nanofiber aerogel derived from ultralight biological materials. Using the new method of "3d network reconstruction" of nano-fibers, the electrostatic spinning nano-fibers and new biomass carbon sources were constructed into ultra-lightweight and super-elastic carbon based nano-fibers aerogel, which has a honeycomb mesh structure, and its solid material density is only 0.14mg/cm3. Article source and network
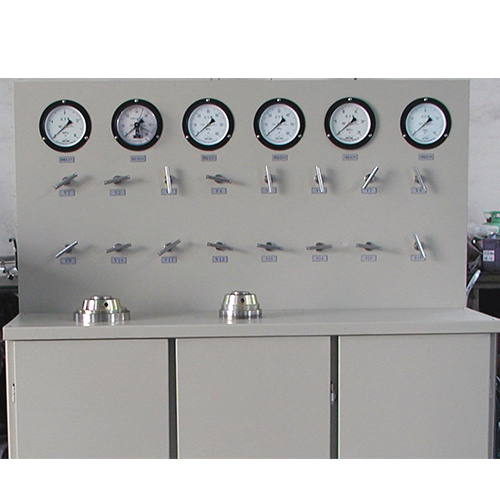

Aerogel equipment
The address of this article:/en/news/393.html
Key word:Carbondioxideextraction,Aerogelequipment,Supercriticalfoamingequipment
Recently, browse:
Related products:
Related news:
- The development of supercritical fluid
- A brief explanation of supercritical extraction
- Product characteristics of supercritical fluid
- Classification of reaction vessels
- What factors affect extraction
- The application of carbon dioxide
- An overview of carbon dioxide
- Supercritical CO? solvent content
- 9/5000 The way carbon dioxide is produced
- What are the characteristics of supercritical carbon dioxide